1.1 General Safety Information
The working principle of a CO₂ Laser
LASER stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. The AEON NOVA Super Redline series uses a CO₂ laser, which operates by electrically stimulating molecules in a carbon dioxide gas mixture. This gas mixture typically includes carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen, and helium. When electricity passes through the gas, it energizes the molecules, causing them to emit light particles, or photons. As these photons interact with other molecules, they create a chain reaction that amplifies the light, producing a highly focused and intense laser beam. Once this laser beam is directed and focused through a special lens, it becomes capable of vaporizing a wide range of materials, from wood and acrylic to fabrics and certain metals. By controlling the speed, intensity, and focus of the laser beam, operators can achieve different results: lower speeds and higher power are used for cutting, while higher speeds and lower power are generally used for engraving. This flexibility makes the AEON NOVA Super Redline series an ideal tool for precise, detailed cutting and engraving across a variety of materials.

1.2 Safety Lock System
The AEON NOVA Super Redline series is designed with a highly effective safety interlock system to protect users during operation.
The AEON NOVA Super Redline series is designed with an advanced safety interlock system to protect users during operation. This system uses magnetic sensors located on the lower corner of the laser working window, near the acrylic lid. When the lid is open, these sensors automatically deactivate the laser, immediately stopping the emission of the laser beam to prevent accidental exposure or injury. Once the lid is securely closed, the magnetic sensors detect the change in position and reactivate the laser system, allowing the operation to resume.
This safety mechanism is essential for ensuring user protection, especially during tasks that require adjustments, material loading, or other maintenance actions inside the laser work area. This safety interlock is a vital part of the machine's safety system, especially during tasks requiring adjustments, material loading, or maintenance. Additionally, operators should observe all standard laser safety practices.
1.3 Safety Precautions:
Overview of Safety and Risk Management
The AEON NOVA Super Redline series laser engraving system uses a Class 4 carbon dioxide (CO₂) laser that emits highly intense and invisible laser radiation. Without proper safety precautions, exposure to this laser radiation – either direct or diffuse reflections – can be dangerous.
Risks Associated with Laser Exposure:
Eyes: Direct exposure can cause burns to the cornea, leading to severe eye injury.
Skin: Can cause burns upon contact with the laser beam or scattered reflections.
Clothing: Presents a fire hazard if exposed to laser radiation.
To ensure safety and machine integrity, unauthorized modifications or alterations to the laser system are strictly prohibited. Altering the machine in any way can compromise safety and will void the manufacturer’s warranty.
Fire Safety Measures
Fire Extinguishers: A CO₂ fire extinguisher should be placed near the laser system.
Avoid Flammable Materials: Avoid storing flammable materials inside the machine, and remove any leftover material after each use to prevent fire risks.
Constant Supervision: The machine must never be left unattended while in operation, as small scraps and debris can ignite and cause damage if not monitored. Environmental Requirements: The machine should be placed in a clean, dry, and stable environment, free from pollution, extreme electrical currents, and magnetic fields.
Limit Switch and Safety Devices: Do not disable or tamper with the limit switch or any safety devices. Doing so may void the machine's warranty and pose significant safety risks to the operator and the machine. Do not leave the laser unattended: Never leave the laser unattended while it is in operation. Small debris or residue left behind can ignite, potentially causing damage to the machine if not promptly addressed.
Stable Power Supply: Only operate the machine when the power supply voltage is stable and matches the machine’s specifications. Unstable or mismatched power supplies can lead to malfunctions or damage to the equipment.
It should also be kept within the following conditions:
Temperature: 5–40°C
Humidity: 5–95% (non-condensing)
This safety interlock is a vital part of the machine's safety system, especially during tasks requiring adjustments, material loading, or maintenance. Additionally, operators should observe all standard laser safety practices, such as:
- Wearing laser safety goggles as required.
- Keeping hands and tools away from the laser path.
- Operating the machine exclusively with trained personnel
- Do not disable or tamper with safety features, such as interlock systems These built-in safety features of the AEON NOVA Super Redline series, in conjunction with standard safety practices, help ensure a secure, reliable, and efficient working environment.
1.4 Safety & Warning Labels
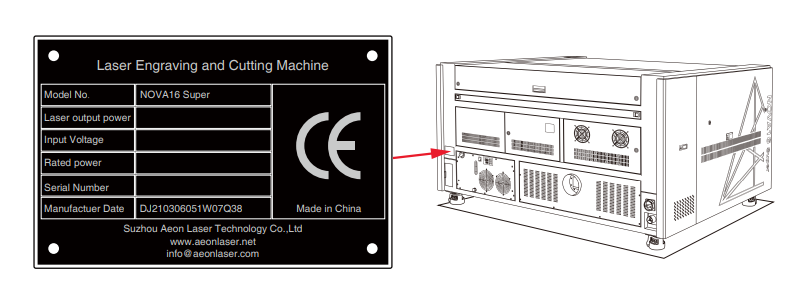
Manufacturer’s Label
On the right rear side of your AEON NOVA Super Redline machine, you’ll find the manufacturer’s label, which includes key details like the serial number, model, laser power, and electrical specifications. Before reaching out for technical support, make sure to have this information ready, as it helps the service team provide the correct assistance for your specific machine.
Safety Warning Labels
AEON Laser prioritizes the safe operation of our machines and is committed to providing the highest level of safety. While our machines are designed to be safe under normal operating conditions, we have added warning labels both inside and outside the machine to ensure safety in case of any unforeseen accidents. These labels indicate areas where extra caution is necessary, and users should pay special attention to them before operating the machine. Our labeling system uses both symbols and text to attract users' attention and clarify the meaning of each label. The following symbols are included to help users quickly understand safety instructions.



Before operating the machine, users should familiarize themselves with these labels and exercise extra caution wherever a warning label is affixed. Following these safety warnings will help ensure a secure working environment and reduce the risk of accidents
1.5 Safety Materials
Laser machines rely on high heat to cut or etch materials. While some materials respond well to this method, others do not and can release harmful gases when heated. It is essential to know the properties of the material you are using, as certain materials (like PVC) may cut easily but release toxic chlorine gas, which is hazardous to both humans and the machine. Below is a general guide to help determine safe materials for laser processing. Since new materials are constantly being introduced, if you are unsure about the laser's compatibility with a material, please contact us. We will assess its safety and performance to ensure it can be processed without risk.
Plastics:
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)----good for engraving and cutting
- Acrylic (also known as Plexiglas, Lucite, PMMA)----good for engraving and cutting
- Delrin(POM, Acetal)---- good for engraving and cutting
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) ---- Melts poorly, not very good for cutting or engraving.
- Kapton Tape (Polyimide)---good to use
- Mylar (Polyester)---good to use
- Nylon – Melts poorly, not recommended
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)----good to use
- Polyethylene (PE) – Melts poorly, not recommended
- Polypropylene (PP)– Melts somewhat, not recommended
Styrene Two-tone acrylic-top color different from the core material, usually for custom instrumentation panels, signs, and plaques. Good for laser processing
Foam
Depron foam-often used for RC planes, good for laser processing EPM
Gator foam- foam core gets burned and eaten away compared to the top and bottom hard shell.
Other:
- Cloths(leather, suede, felt, hemp, cotton)
- Papers
- Rubbers(only if they do not contain chlorine Teflon(PTFE, Polytetrafluoroethylene)
- Woods(MDF, balsa, birch, poplar, red oak, cherry, holly, etc)
Materials that can’t or should not be cut
- Metals
- Polycarbonate(PC, Lexan)due to the fumes
- Any materials containing chlorine: a. PVC(Cintra)-contains chlorine b. Vinyl- contains chlorine, high-pressure materials include all the above guidelines, and as listed:
- Stainless steel: up to 18 gauge
- Mild steel: up to 18 gauge
- Thicker and Denser woods
Below is a chart of some frequently processed materials by CO2 laser machines:
* CO2 lasers can engrave or mark coated metal. For bare metal, it is not recommended, as the laser light might reflect back into the laser path, causing permanent damage to the optical parts. However, there are CO2 laser marking solvents available on the market. After applying these solvents, it is safe to use a CO2 laser for marking